source : Robotics Fundamentals Series: CCDs and CMOS Image Sensors - Developer Zone - National Instruments
CCDs and CMOS image sensors are increasingly used in robotics. Autonomous robots utilize cameras to track objects and identify movement characteristics. Unmanned vehicles that competed in the 2007 DARPA Grand Challenge used cameras in conjunction with LIDAR to identify objects in the environment in order to safely drive through the course. In the DARPA Urban Challenge, cameras were used in order to identify curbs and lane lines to keep the unmanned vehicles within lanes as they moved through an urban environment. CCDs and CMOS image sensors use photo-active regions to read light characteristics in order to generate images. They provide the capability for environmental analysis, navigation, object identification and tracking. CCDs use a lens to direct light onto an array of capacitors which develop a charge that is proportional to the intensity of the incoming light. This charge is then transported across the exposed region and converted to voltage. These voltages can be used to recreate the image. CMOS image sensors consist of an array of pixels built from transistors and a photodiode. The photodiode transforms the incoming light into a voltage. One transistor is used to reset the pixel for each image acquisition. Another serves as an amplifier so the signal is visible to the processing electronics. A third transistor is used as a switch so that a row of pixel voltages are sent to the processing electronics. Color information is recorded with one of two ways. One method is to use three sensors, each dedicated to detecting the intensity of one of the three primary colors. The three images are added together to create the final image. The second is to use filters to isolate the primary colors of the incoming light. The sensor makes three acquisitions, one for each primary color, and adds them together for the final image. For more information on camera sensors, refer to Anatomy of a Camera at ni.com/zone. 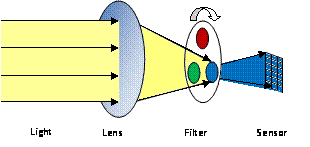
Figure 1. Image Sensor Setup to Capture Blue Component Both image sensors can be used for most applications. However, there are advantages to both: CCD - Higher quality images with little noise
- Typically more pixels
- Higher sensitivity to light
CMOS - Lower cost
- Easier to build
- Lower power consumption
Robotics applications using both CCD and CMOS image sensors can be implemented with LabVIEW and National Instruments products. Virginia Tech's team Victor Tango's entry in the 2007 DARPA Urban Challenge used LabVIEW to control their vision systems and analysis of image data. Drivers and software are available for both NI Vision products as well as third-party sensors including the Point Grey Research Firefly MV and Firefly 2. Refer to National Instruments Industrial Camera Advisor for more information on using third-party cameras with National Instruments hardware.
Labels: Camera, CMOS, Robotic, Thèse, tracking sensors
|
